When it comes to getting the best performance out of your computer, few upgrades provide as much of a noticeable boost as overclocking your CPU. By pushing your processor to run faster than its default speed, you can increase your system’s performance in resource-intensive tasks like gaming, video editing, and running complex applications.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through the process of overclocking your CPU to maximize its performance, ensuring a smoother and faster computing experience.
What Is CPU Overclocking?
CPU overclocking is the process of increasing the clock speed of your CPU beyond its manufacturer-rated speed, known as the base clock. This is done to make the processor perform faster, allowing you to get more power out of the same hardware. Overclocking increases the performance of the CPU, which directly impacts the overall speed and responsiveness of your computer.
However, overclocking is not without its risks. When you push your CPU to work harder, it generates more heat and consumes more power. If done incorrectly, it can lead to system instability or even permanent damage to the hardware. But, with proper planning and precautions, overclocking can be a relatively safe and highly rewarding process.
Why Should You Overclock Your CPU?
There are several reasons why you might want to overclock your CPU for maximum performance:
Improved Gaming Performance: Overclocking your CPU can have a significant impact on gaming performance, especially in CPU-intensive games or titles that require faster processing power. By increasing your CPU’s speed, you can get higher frame rates and smoother gameplay.
Better Multitasking and Productivity: If you’re running multiple programs simultaneously or working with heavy applications like video editing software, overclocking can help boost performance and speed up tasks.
Future-Proofing Your System: As software demands continue to increase, overclocking can provide a cost-effective way to keep your system up to date without the need to invest in new hardware immediately.
Enhanced Benchmark Scores: If you’re into benchmarking, overclocking can help you achieve higher scores, which can be useful if you want to show off the performance capabilities of your system.
What You Need to Overclock Your CPU
Before diving into overclocking, you need to ensure that you have the right hardware and tools to perform the task safely. Here’s what you’ll need:
1. A CPU That Supports Overclocking
Not all CPUs are designed for overclocking. Intel’s “K” and “KF” series processors, such as the Intel Core i7-12700K, are unlocked for overclocking, meaning you can push them beyond their base speeds. Similarly, AMD Ryzen processors with the “X” or “XT” designation are typically unlocked and ideal for overclocking.
2. A Compatible Motherboard
Your motherboard needs to support overclocking. High-end motherboards, especially those built for gaming and enthusiast PCs, usually have advanced power delivery systems and cooling features designed for overclocking. Look for motherboards with chipsets like Intel’s Z-series or AMD’s B-series and X-series, which allow CPU overclocking.
3. Effective Cooling System
Overclocking generates extra heat, and a good cooling system is essential to prevent your CPU from overheating. Stock coolers that come with most CPUs may not be sufficient for overclocking. Consider investing in high-performance air or liquid cooling solutions, especially if you plan on pushing your CPU to its limits.
4. Stable Power Supply
An overclocked CPU demands more power, so it’s crucial to have a high-quality power supply unit (PSU) with adequate wattage to support the increased power consumption. Make sure your PSU has enough headroom to handle the additional load.
5. Overclocking Software and BIOS Access
Overclocking can be done through BIOS/UEFI or using software provided by your motherboard manufacturer. Software like Intel’s Extreme Tuning Utility (XTU) or AMD’s Ryzen Master allows you to make adjustments from within your operating system. However, for more precise control, BIOS settings are typically preferred.
Step-by-Step Guide to Overclock Your CPU
Once you’ve gathered all the necessary hardware, it’s time to start overclocking your CPU. Below is a step-by-step guide on how to achieve maximum CPU performance safely.
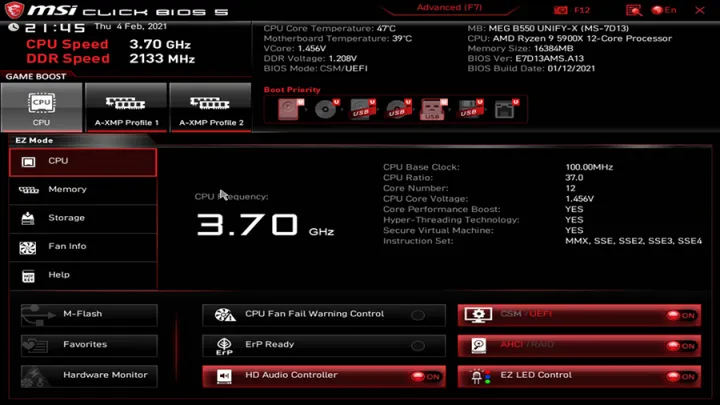
Step 1: Enter the BIOS/UEFI
To begin overclocking, you’ll need to access your computer’s BIOS/UEFI settings. You can do this by restarting your computer and pressing the BIOS key (usually “Delete” or “F2”) during the boot process.
Step 2: Adjust the CPU Multiplier
In the BIOS, locate the CPU settings. You’ll need to find the CPU multiplier, which determines the overall speed of the processor. By increasing this multiplier, you increase the clock speed of your CPU. Start with a small increase (around 100 MHz) to avoid pushing your system too far.
Step 3: Increase CPU Voltage
As you increase the CPU multiplier, the processor will require more power to maintain stability. To achieve this, increase the CPU core voltage (Vcore) slightly. Be cautious, though – too much voltage can damage your CPU. A good starting point is to increase the voltage in small increments, testing stability after each adjustment.
Step 4: Stress Test the CPU
After making changes to the CPU multiplier and voltage, it’s crucial to stress test the system to ensure stability. Use stress-testing software like Prime95, AIDA64, or IntelBurnTest to push the CPU to its limits and check for stability issues like crashes, freezes, or system errors.
Step 5: Monitor CPU Temperatures
During stress tests, keep an eye on the CPU temperature using software like HWMonitor or Core Temp. Temperatures should stay below 85°C under load. If temperatures rise too high, you may need to reduce the overclock or improve your cooling solution.
Step 6: Fine-Tune the Overclock
If your system passes the stress test and remains stable, you can fine-tune the overclock by tweaking the settings further. This process involves finding the perfect balance between speed, voltage, and temperature for optimal performance. Repeat stress tests after each adjustment to ensure stability.
Step 7: Long-Term Stability Testing
Once you’ve achieved the desired overclock, perform a longer stress test (several hours) to ensure your system remains stable under prolonged use. If your system crashes or exhibits instability, reduce the overclock or adjust the voltage until it becomes stable.
Troubleshooting CPU Overclocking Issues
Even with careful adjustments, overclocking doesn’t always go smoothly. Here are some common issues you may encounter and how to resolve them:
- System Crashes or Freezes: If your system crashes during a stress test, it’s likely due to insufficient voltage or excessive overclocking. Reduce the multiplier or lower the voltage in small increments.
- High Temperatures: If your CPU temperature exceeds safe limits, it’s a sign that your cooling solution isn’t sufficient. Either lower the overclock or upgrade your cooling system to handle the increased heat.
- Instability: If your system experiences instability during normal use, try lowering the overclock slightly or increasing the CPU voltage.
How Overclocking Affects CPU Performance in the Long Run
While overclocking can provide significant performance boosts, it’s important to understand the long-term effects. Overclocking increases the wear and tear on your CPU due to the higher power and heat levels it generates.
Over time, this can potentially reduce the lifespan of your processor, although the effects may not be significant enough to worry about in the short term. To mitigate this, it’s essential to keep an eye on temperatures and ensure your system remains properly cooled.
Should You Overclock Your CPU?
Overclocking can unlock substantial gains in CPU performance, especially for gaming, creative tasks, and multitasking. However, it requires careful planning and the right hardware to avoid damage and instability.
If done correctly, overclocking can breathe new life into your system, providing a faster and more responsive experience. As with any modification, there are risks, but with the right tools and knowledge, you can achieve an optimal balance of speed and stability to maximize your CPU performance.